What Material Makes A Urethane Wheel Not Squeak For Camera Dolly
Urethane Wheels
Introduction
This commodity will accept an in-depth await at urethane wheels.
The commodity will bring more than detail on topics such equally:
- Principle of Urethane Wheels
- Types of Urethane Wheels
- Applications and Benefits of Urethane Wheels
- And Much More…
Chapter 1: Principle of Urethane Wheels
This affiliate will discuss what urethane wheels are, their construction, and how they function.
What are Urethane Wheels?
Urethane wheels are wheels made of molded urethane, also known as polyurethane. Urethane is an elastomer that comprises urethane carbamate linkages and is a portmanteau phrase for "rubberband polymer."
All of the advantages of metallic, plastic, and rubber wheels are integrated in urethane wheels. They are more price effective, more flexible, have better dissonance reduction, college resilience, and are more resistant to affect, chafe, and corrosion than metallic.
In terms of low temperatures, impact, cold flow, abrasion, and radiations resistance, urethane outperforms plastic. They can besides reduce noise, are more than resilient, take superior elastic memory, and are less expensive than plastic. Finally, due to its wider range of hardness, ease of customization, and superior bear upon resistance, urethane surpasses safe. Polyurethane wheels tin also be retooled and recoated, reducing the need for costly fine tuning.
Polyurethane Molding
Urethane wheels come up from polyurethane molding is the process of placing a urethane polymer organisation into a tool or mold and allowing it to cure in order to fabricate or manufacture plastic items. Polyurethane'southward exceptional processability makes it a particularly effective fabric in the industry of typical consumer goods and industrial parts, just like any other type of plastic. Polyurethane molding can readily reach tight tolerances and complex shapes, which include urethane wheels.
Polyurethanes are incredibly adaptable materials that may exist formulated in a variety of means to produce a diverseness of plastic characteristics. They can have a wide range of mechanical qualities, from soft and malleable to hard and rigid. They can also exist made into high-performance, engineering-grade appurtenances using certain compounds.
The Construction of Urethane Wheels
This section volition discuss the construction of urethane wheels.
Urethane Fabrication Process
In the fabrication process urethane wheels are constructed by combining typically standardized parts using two private processes.
Liquid Casting
Urethane is melted to a liquid country and then poured into a bike-shaped mold to cool and harden. In this process, constructed resins can also be used. The liquid casting method is commonly used for prototyping and pocket-sized-scale manufacturing.
Injection Molding
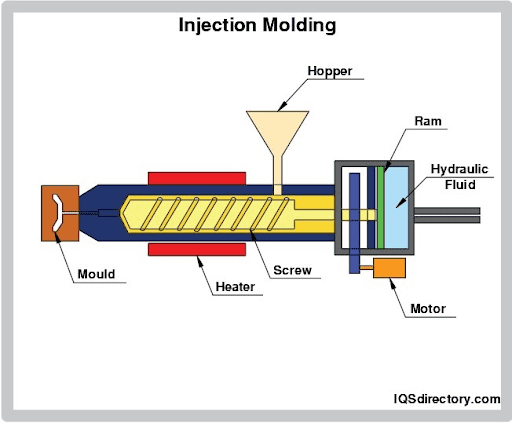
It entails melting the urethane to a liquid state and injecting the liquid material into a cycle-shaped mold through fill holes with a low-force per unit area pneumatic injection gun. Injection molding machines are made up of a complex network of motors, heaters, and other moving parts that swallow a lot of energy to run. However, enquiry has been washed to improve the energy efficiency of this process. Regardless, injection molding takes for around 32 percent of all plastic processing applications and is 1 of the most prominent plastic processing techniques today.
Secondary Fabrication Processes
Secondary methods tin likewise exist used to brand urethane wheels from molded urethane. Urethane wheels can exist produced from solid urethane or a mixture of urethane and metals including cast fe, aluminum, and steel. For heavier-duty applications, these wheels are ideal. The core of a bonded-to-metal bicycle is synthetic of metallic, while the tread is fabricated of urethane. Urethane wheels are extremely cost-effective to manufacture, and the FDA has allowed their usage in clean rooms and other sterile situations.
Urethane Materials
Although polyurethane is a polymer variant of urethane, the two materials are substantially the same. Polyurethanes are fabricated upward of several components. Polyols and diisocyanates are the main components. Other components include curatives and additives that give a polyurethane polymer limerick its distinctive qualities. Blowing agents, surfactants, and catalysts are further components unique to polyurethane foams that aid in the generation of gasses needed to form the foam's structure.
Prepolymer Organisation
Polyurethanes are made up of many materials. Polyols and diisocyanates brand up the majority of the mixture. Curatives and additives are other components that give a polyurethane polymer limerick some of its item qualities. Blowing agents, surfactants, and catalysts are some other group of components unique to polyurethane foams that assist in the generation of gasses necessary for the foam's structure.
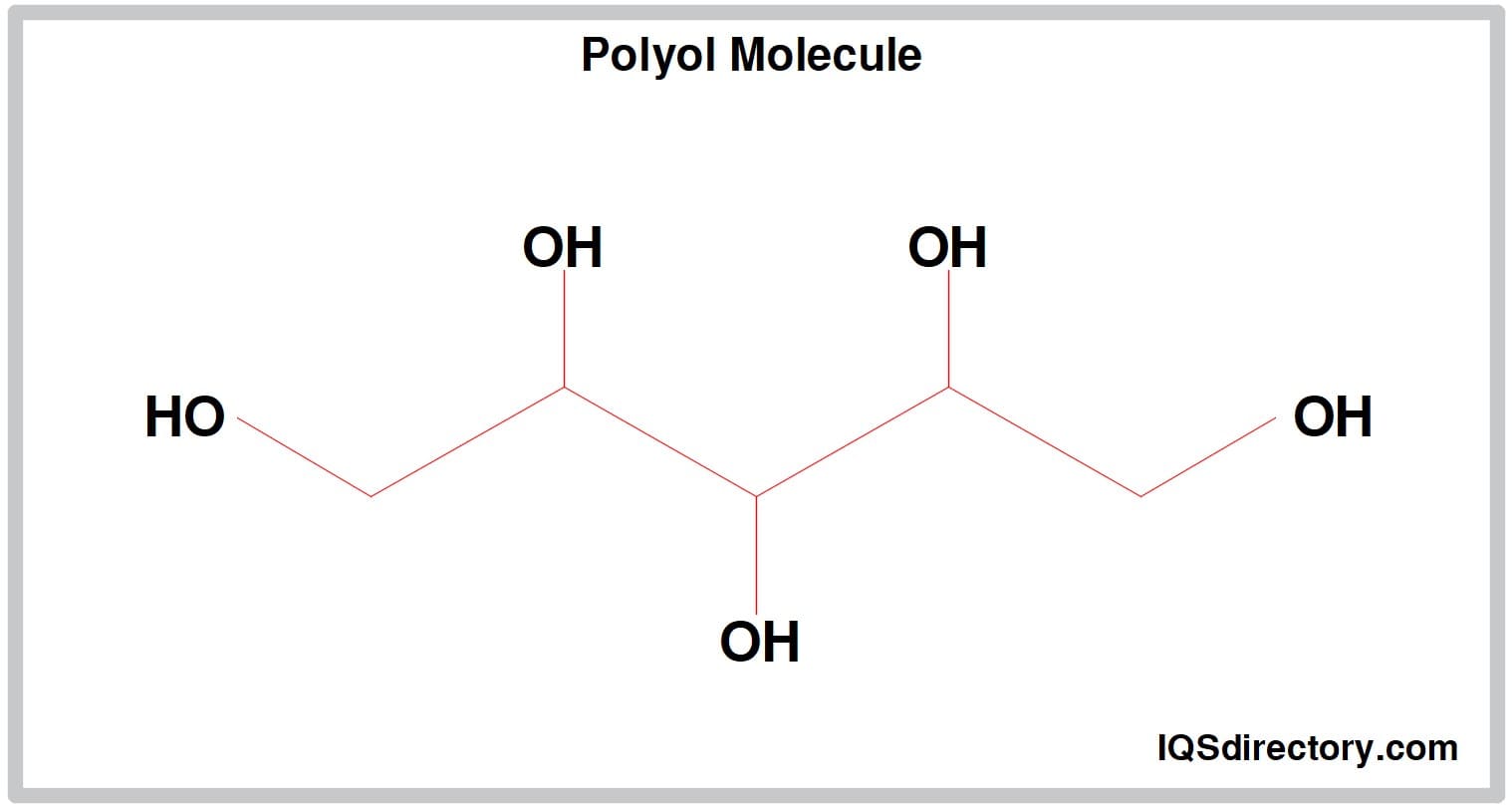
Polyol in Urethane Wheels
An organic molecule with ane or more hydroxyl (OH) groups is known as a polyol. Polyether or polyester polyols are the ii types of polyols used in urethane casting.
Polyether Material
The interaction of organic oxides with glycol produces these. Polyether is distinguished by its stiff impact resistance, minimal heat build-upwardly for dynamic applications, hydrolysis resistance, and low-temperature functioning. PTMEG and PPG are ii forms of polyether often utilized in the polyurethane industry. PTMEG is the better of the two, only it is too the more than expensive.
Polyester Urethane Material
The polycondensation reaction of di-acids and glycol produces these. Polyesters have meliorate chafe resistance, oil resistance, oestrus aging resistance, shock absorption qualities, solvent resistance, and tear resistance than polyether.
Specialty Polyols
Polycarbonate and polycaprolactone polyols are the about frequent. Polyesters are a type of polyol that includes these two polyols. Because of their strength and hardness, polycarbonates are employed as engineering materials. Polycaprolactone, on the other mitt, provides excellent water, oil, solvent, and chlorine resistance to cast urethane.
Diisocyanate Compounds
Diisocyanate compounds, similar polyols, make up the resin side of the polyurethane system. Aliphatic and aromatic diisocyanates are the 2 basic forms of diisocyanate.
Aliphatic Diisocyanates
The non-yellowing appearance of this type is its most appealing feature. They besides have a lower reactivity, making them suitable for chemical-resistant coatings. Where color stability is required, aliphatic diisocyanates are commonly employed in polyurethane coatings, castings, and films. Hexamethylene (HMDI), Hexamethylene (HDI), and isophorone are the near frequent ADIs (IPDI).
Aromatic Diisocyanates
Aromatic diisocyanates correspond more than than 90% of total diisocyanate consumption. This kind is further divided into TDI, NDI, and MDI.
Polyurethane Foam Components
These are features that are specific to polyurethane foams. Bated from the prepolymer organisation of polyols and diisocyanates, bravado agents, surfactants, and, in some blends, catalysts are required to manufacture the product. These boosted raw components produce foaming gasses and manage them in order to become the desired foam construction.
Blowing Agents
Blowing agents are employed to generate gas, which is and so used to create the cream'south cellular structure. Gas can be introduced into the polymer system chemically or physically. CFC-11, often known every bit trichlorofluoromethane, was the starting time blowing agent utilized. Because of its non-combustibility, acceptable boiling indicate, skilful compatibility with polyurethane, and lack of toxicity, this was regarded as an ideal blowing agent. However, the molecule, along with other hydrochlorofluorocarbons, was banned by the Montreal Protocol in 1987 due to its ability to deplete the ozone layer. Water, pentane, methylene chloride hydrocarbons, halogen-free azeotropes, and other goose egg ozone depletion-potential blends are currently replacing CFCs.
Surfactant Additives
Surfactants are additives that aid in the formation, stabilization, and setting of polyurethane foams. Silicone-based surfactants are the near usually utilized. Silicone surfactants perform critical roles such as lowering surface tension, preventing cream collapse till cantankerous-linking, managing cell size, limiting cell shrinkage after cure, and compensating for whatsoever deformities caused past the add-on of particles to the solution.
Urethane Catalysts
Catalysts are used to control the rate of isocyanate and hydroxyl group reaction as well as the rate of gas generation. These polymerization and gas generation operations must commonly take place at the same fourth dimension. If the polymerization procedure is faster than the gas generation process, the cells tend to stay close together, causing the foam to compress as information technology cures and cools. As a event, if the gas generation rate is faster, the cells expand earlier the polymer tin cure and sustain them. To produce compatible open up cells, the speeds of these two reactions must exist balanced.
Curative and Chain Extenders
Curatives and concatenation extenders are used to crosslink the lengthy, chained molecules generated by the polyol-diisocyanate procedure. They are combined with the prepolymer organisation of polyol and diisocyanate to form a solid or semi-solid elastomer. They are present in the majority of thermosetting polyurethane compositions. Hydroxyls and amines are the 2 most common forms.
Hydroxyls (Diols)
The hydroxyl groups at the molecule terminals that link prepolymers are nowadays in these curatives. At room temperature, the standard hydroxyl curative is ane,four-butanediol (BDO), which is often employed in MDI prepolymer systems.
Amines
Aside from hydroxyl groups, amine groups can likewise link to the prepolymer terminals. As the basic curative for TDI prepolymer systems, the virtually commonly used amine curative is 4,four-methylenebis (2-chloroaniline) or MOCA. OSHA, on the other mitt, designated this type as a carcinogen. Other amine chain extenders, such every bit 4,four-methylenebis (3-chloro-2,six-diethylaniline), are currently in employ.
Using Additives
Additives are used to requite the polyurethane product additional properties. The kind and amount of condiment are chosen based on the conception of the polymer organisation and the intended apply. Some polyurethane additives are fillers, plasticizers, stabilizers, antistatic agents, degassing aids, flame retardants, pigments, and colorants.
How Urethane Wheels Office
When opposed to tougher wheels such as steel or bandage iron, urethane wheels are a preferred option in industrial applications due to their quiet functioning. The urethane functions equally a stupor cushion and cushioning amanuensis. Information technology also absorbs the bumps acquired by uneven terrain. When OSHA rules apply, adopting urethane wheels instead of steel or cast iron wheels can dramatically lower noise levels, helping to protect employees' hearing.
When compared to rubber, urethane tires are commonly used for their load-begetting capabilities. Urethane has a higher load-bearing capability while notwithstanding offering the advantages of a rubber tread, such as daze absorption, noise reduction, and flooring protection.
Urethane deflects and leaves a much bigger presence than tougher bicycle materials like nylon. This increased surface area reduces shear force on floors and keeps them in splendid shape for longer durations. Urethane wheels also function by providing better traction and grip, reducing the load on the bike to provide the required driving force.
Specifications of Urethane Wheels
If these specifications are considered, a skilful experience with urethane wheels is likely in industrial use.
Urethane Temperature
When utilized properly, polyurethane is an extremely robust substance. All the same, when utilized in loftier environmental temperature applications or applications that create heat, the urethane's durability is drastically reduced. Most ordinary urethane cannot survive temperatures higher up 110 degrees Celsius for more 60 to xc minutes without being damaged. Internally generated heat (from cyclic urethane deflection) in the 121 caste range volition liquefy the material in fifteen minutes.
Urethane Type
Polyurethane utilized in industrial applications must have qualities that outperform many urethanes being used in non-dynamic applications. In guild to get the best urethane for needed purposes, the post-obit factors must be considered: tensile strength, tear forcefulness modulus, and chafe resistance.
Hot Casting
The merely mode to produce an industrial wheel is by hot casting. Hot cast urethanes (poured at 60 to 76 degrees Celsius and cured at 87 to 114 degrees Celsius) produce a stronger wheel for demanding dynamic applications. Room-temperature produced and cured urethanes rarely provide the concrete qualities required in an industrial wheel application.
Considerations When Choosing Urethane Wheels
Some of the considerations when choosing urethane wheels include:
Load Capacity
Each wheel has a minute indicate of contact with the surface it is rolling on. As a result, weight distribution is crucial. An overloaded bike will deform over time, increasing friction and resistance and eventually failing. Agreement and preparing for the highest load will help in the selection of the appropriate bicycle.
Surface Conditions
Urethane wheels, despite being robust and forgiving on rougher surfaces, are influenced by the surface on which they are running. A dissimilar fabric or diameter may exist preferable depending on whether the bike is operating on smooth concrete or over rougher terrain. Aside from mechanical problems, wheels may come into contact with chemicals. Although urethane performs extraordinarily well in this climate, information technology is still a gene to consider.
Surface Traction
Braking and acceleration are expected and may bear on the specification, particularly if these parameters are extreme or precise. It is necessary to maintain regular, anticipated traction while maintaining stable contact with the rolling surface. Urethane wheels provide superior traction. However, traction can be reduced in detail circumstances where maintenance issues cause dust, grease, or oils to accumulate. These ecology concerns should be addressed throughout the planning stage. A consistent cleaning strategy for surfaces and tracks helps extend the life and efficiency of wheels.

Operating Temperature
Urethane wheels, like rubber, will expand and contract in reaction to environmental conditions. These temperature ranges are useful in cases where brusk-term exposure to severe temperatures is required, such equally moving in and out of a deep freezer or a mining operation. Special formulas are offered in extreme circumstances to extend wheel life.
Extreme temperatures exterior of the normal range are frequently reversible. Farthermost estrus will permanently destroy a urethane wheel. Operating outside of the depression-temperature spectrum might outcome in brittleness, which can cause irreversible impairment.
Indoor and Outdoor Uses
When moving wheels from indoor to outdoor situations, every ecology variable is introduced into the equation. Temperature, humidity, and the concrete limitations of diverse surfaces are all factors to consider. Transition points oftentimes have saddles or other seams that might wear or harm the wheel. Even though urethane wheels are quite robust and resilient, it is critical to restrict the changes from one surroundings to the next. This helps to proceed the wheel's integrity and prevents delamination. A smoother piece of work area with fewer surface changes can help to increase the life of a bike.
Build-Upwardly on the Wheels or Tracks
Unexpected environmental circumstances are oftentimes to blame for traction loss or wheel deformation. These tin cause aggregating on the bicycle, caster, or even the rails. Whatever urethane bike tin can exist affected by build-up, resulting in premature wheel failure. The simplest method to avoid these scenarios is to thoroughly examine the ventilation arrangement, where air motion could be shifted away from tracks, or perform routine track cleaning.
Touch on and Shock
Wheels may exist subjected to bumps, sudden loads, or lowering in a more enervating environment. Inside the parameters of the formulation, urethane is potent enough to behave bear upon. However, as with any other problem, this might cause wearable to the beam, cycle, or load bearings. The affect is measured in a unlike manner than the load. And, even if the wheel is well-designed for the specified load, it is adequate for bear upon, lowering, or daze. In some circumstances, this may result in a new material design that is more tolerant of damage.
Chapter 2: Types of Urethane Wheels
The types of urethane wheels include:
Crowned Wheels
Crowned poly wheels accept significantly reduced rolling resistance than standard flat treaded wheels. These wheels range from 100 to 200mm and consist of a silent running urethane tire wrapped around a lightweight aluminum center.
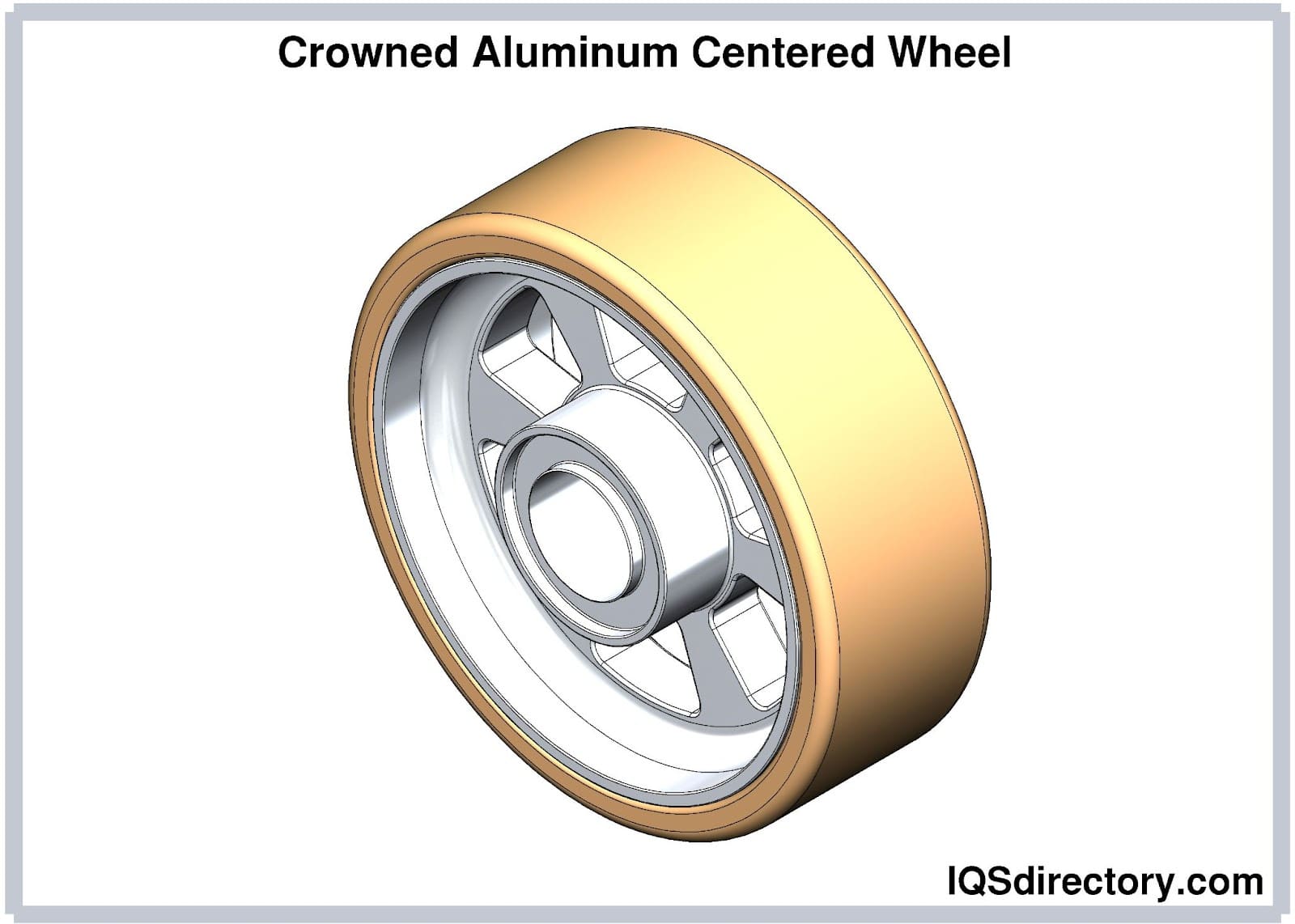
They are also resistant to solvents and annoying wear and accept precision ball bearings for long bearing life. They can concord up to 600kg in load chapters and are typically used in conveyor systems.
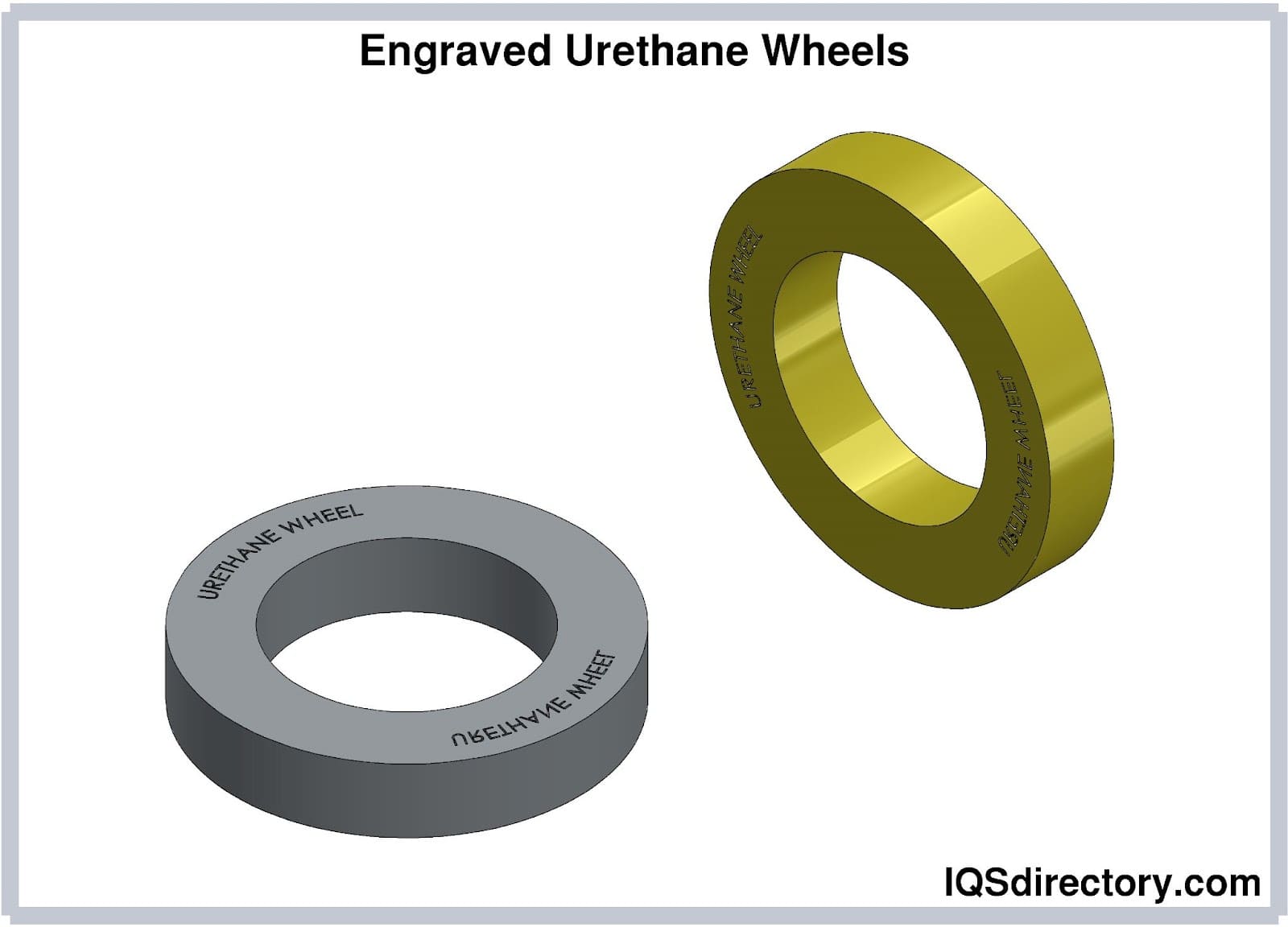
Engraved Wheels
These feature engraved patterns such as brand names, identification marks, or serial numbers. Rolling resistance is higher than that of crowned wheels since they are standard flat treaded wheels. They come in various sizes and have low load chapters.
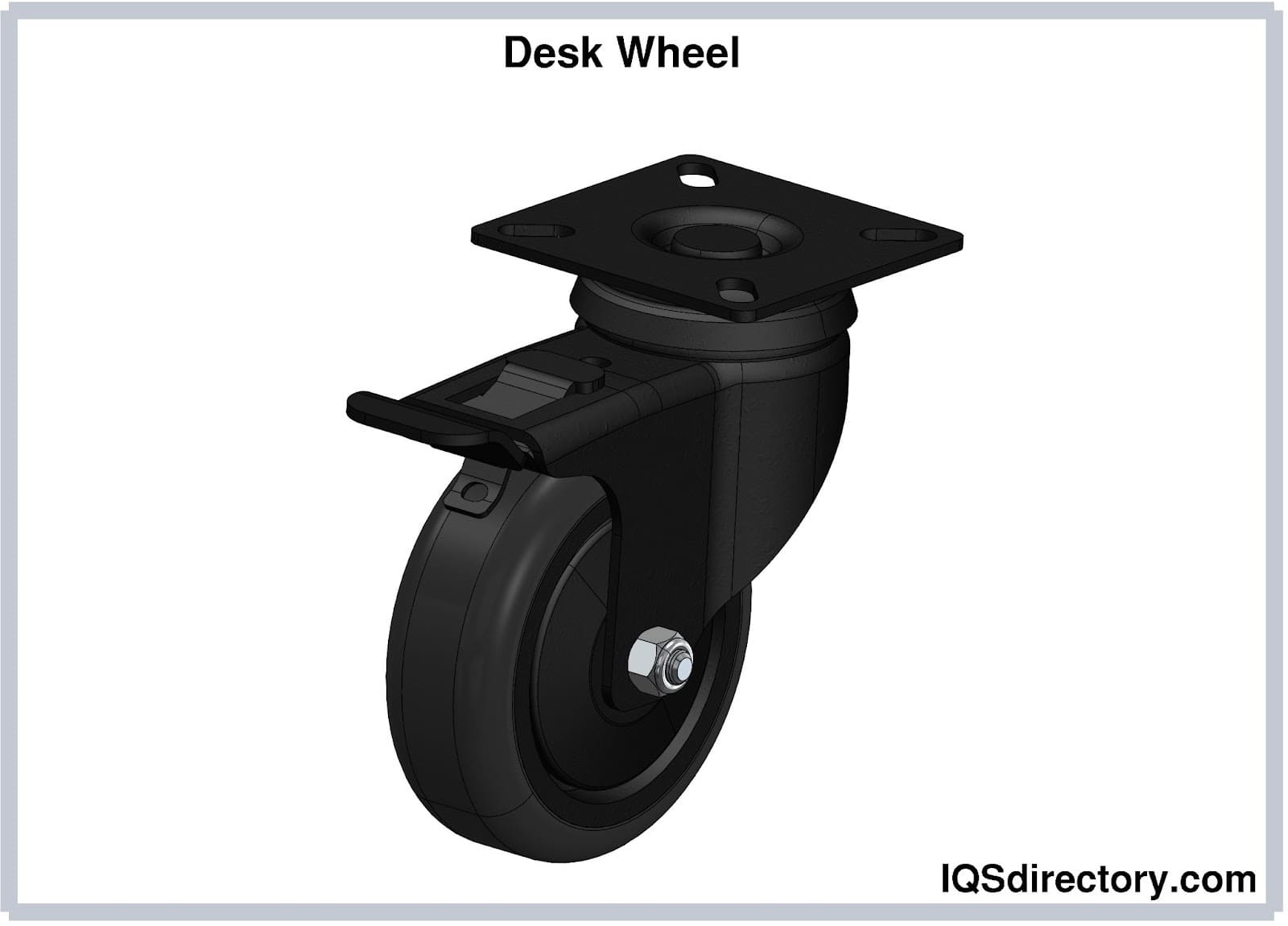
Desk-bound Wheels
These can be plant in document processing equipment. They help in the orientation of your documents for better optical readings. Desk-bound wheels are commonly seen in calorie-free roller applications. Desk Wheels can be utilized every bit soft touch wheels with varying spring rates achieved through the apply of varying urethane harnesses.

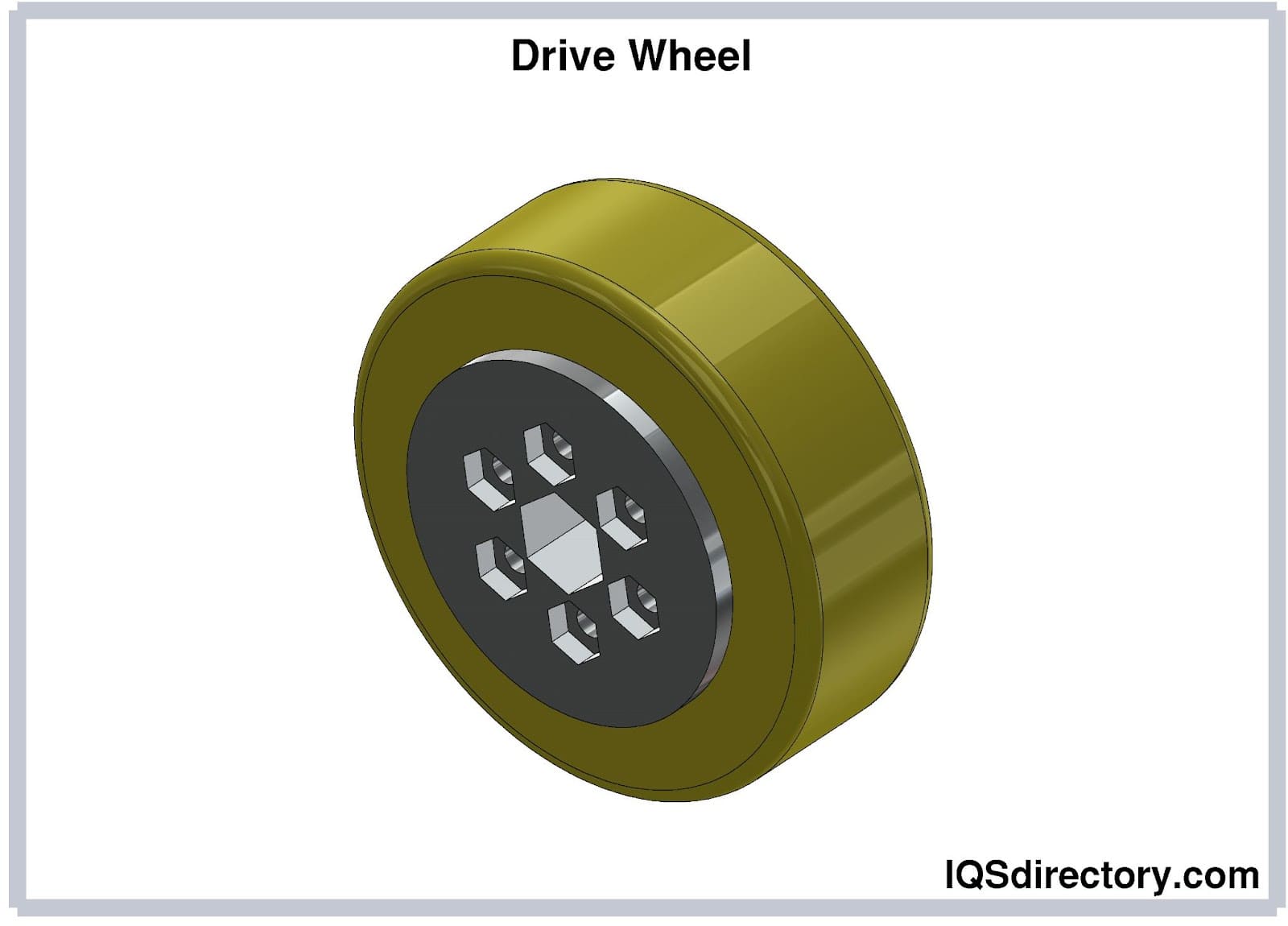
Drive Wheels
Due to the ability to accommodate urethane to any hardness required for the awarding, urethane drive wheels are particularly common. A cardinal slot or bolt to a hub will exist used to drive urethane drive wheels. Urethane bulldoze wheels are widely used in various industries where huge things must be moved apace. When shifting management is required in the awarding, urethane drive wheels work well.
Compliant Wheels
Compliant wheels help make industrial mechanism resistant to abrasion. Compliant Wheels are employed in applications that procedure documents or materials of various thicknesses. Compliant Wheels, with their spring-like motion, enable your gear to process papers of varying thicknesses without the utilize of costly leap mechanisms.
Compliant wheels are also known as no crush wheels, zero crush wheels, and compliance wheels.
Benefits of urethane compliant wheels include:
- Unproblematic machine (springs aren't necessary)
- Serenity performance
- Low maintenance cost
Chapter 3: Applications and Benefits of Urethane Wheels
This chapter will discuss the applications and benefits of urethane wheels.
Applications of Urethane Wheels
The applications of urethane wheels include:
Overhead Conveyor Systems
Overhead conveyors, like many other objects, oft employ wheels to motion items. These wheels are used to transfer products down the rails of overhead conveyors and in conjunction with diverse carrying devices. These track oftentimes contain joints in their structure, which, like expansion joints in a floor, tin cause chunking and tearing. Urethane wheels can withstand a wide range of load requirements while as well resisting clothing, chunking, and tearing. They are designed to exist exactly round and smooth, eliminating habiliment and wobbling.
Industrial Carts
Carts are available in a variety of sizes and strengths to conform a diversity of uses. Urethane wheels are utilized on equipment carts that motion parts and pieces manufactured on automotive assembly lines. For the hefty products they transport, the carts and wheels must have a high load capacity.
Railroad Applications
Urethane wheels are likewise suitable for railroad applications. For case, urethane wheels manufactured by Stellana are used in tugger systems to bulldoze boxcars over train rails. This fabric can run directly on the tracks while providing grip on a very limited surface.
Industrial Washer Systems
A few components work together to dry the wear inside giant industrial dryers. Urethane wheels are used to rotate the pulsate'southward idler wheels. Equally the load dries, these components tumble information technology.
Roll-Forming Machinery
This equipment is used in the metal structure sector to shape metal sheets into rain gutters, siding, metal roofing, and other products. On the equipment, urethane wheels provide two functions. The drive wheel is utilized to describe through the aluminum sheets, while the idler wheels aid in the formation of the necessary angles and bends.
Elevator Uses
Lift contractors adopt the material urethane for their elevator guide wheels. Guide track are installed forth the elevator shaft to move the vehicles during regular operation and to provide backup safety systems. If the cable snaps, elevators take numerous safeguards in place to swiftly halt the auto where it is on the rail. The guide wheels are small wheels that assist the elevator car travel smoothly up and down the rail bars during normal performance.
Hyperloop Uses
Hyperloop is a high-speed transport organization existence developed past Tesla and SpaceX. If pressure is ever lost by the Hyperloop system, interrupting the vacuum formed, urethane wheels would stabilize the vehicle while slowing information technology down from loftier speeds. Fifty-fifty though the vehicle is designed to never affect the basis, urethane wheels perform an important role as a safety feature. This is an application that truly tests the limitations of polyurethane!
Carrying example wheels, conveyor bearings, grocery carts, skateboard wheels, forklift bulldoze, roller coaster wheels, and load wheels are more of the applications for urethane wheels. Medical, athletic equipment, retail, transportation, industrial manufacturing, and material handling are among the industries that benefit from urethane wheels.
Benefits of Urethane Wheels
Molded urethane advantages include exceptional durability due to its resistance to cuts and rips. Information technology is too heat resistant and chemical, dissonance reduction, and elastic memory. The hardness of urethane wheels can vary. They might be sponge soft, iron-difficult, or whatsoever hardness level in between. Aside from hardness, they tin besides be made in a number of colors, sizes, and shapes.
They are resistant to ultraviolet radiation, ozone, oxygen, and a diverseness of other environmental conditions. They are resistant to the effects of abrasive substances. Urethane wears slower than other materials nether the same conditions, making it last longer. Considering the material has higher tensile force, it can withstand heavier loads.
Considering urethane is manufactured chemically, a variety of variants are possible. The density and physical properties of the material can be contradistinct depending on the ultimate usage. The load capacity of urethane wheels is 6 to 7 times that of rubber caster wheels with the same dimensions. Urethane has a loftier elastic retentiveness. Considering of the material's flexibility, it may be employed in a variety of situations where plastic falls curt.
It tin achieve automatic and continuous production with low waste in the apply processes and manufacturing. More essentially, some of the waste residues can exist recycled for new urethane products, which volition not pollute the environment. Liquid casting is a simple manufacturing procedure belonging to the new no cord casting wheel, likewise known as the green wheels of the twenty-beginning century. Urethane wheels will be the time to come developing trend in automotive tires, with numerous applications in the automobile sector.
Drawbacks of Urethane Wheels
Failures of urethane wheels on bulldoze wheels, industrial rollers, and industrial pulley wheels toll companies not only money to replace the wheels but as well equipment downtime. Most of these failures are avoidable, including:
Delaminating Polyurethane Cycle Tread
Polyurethane is often chemically fastened to a plastic or metal substrate in a bicycle or roller application. Delamination happens when the tread separates from the cycle or hub of the roller. In some circumstances, this might be attributed to a poor administration of an adhesive prior to the application of the polyurethane to the hub. Overheating the cycle or exposing it to h2o and/or solvents at the bonding line can also cause information technology. Furthermore, some hub materials are difficult to bail. If adhesive was properly placed, no external weather interfered with the bonding procedure, and the tread is still delaminating, a mechanical bond may be a preferable alternative.
Apartment-Spotting the Cycle
When the bike is loaded in a stationary position, a flat area on the polyurethane tread can occur. When the wheel resumes spinning, this expanse may or may not "gyre-out." It will be more than difficult to move the wheel from a halt in either case. The compression ready value of a polyurethane cloth determines its susceptibility to flat-spot. The problem could be solved by using polyurethane with lower compression set settings. Another option is to utilize a larger bore or breadth wheel, which minimizes the stress on the urethane.
Accident-Out Issues
When urethane treads are subjected to cyclic loading and unloading, estrus is created by friction inside the textile due to the urethane's mechanical hysteresis. If the heat accumulation is too great (more heat created than can be dispersed), the urethane tire volition melt internally, causing pressure to build up as the fabric expands, resulting in a accident-out. Almost of the time, this is acquired past operating the wheel or roller at an excessively fast speed or overloading the part. Information technology may besides be caused by unequal wheel or roller loads. The remedy would be to switch to urethanes with lower heat generation backdrop, raise the diameter, width, or adjust other performance parameters of the bike.
Tread Not bad
If the wheel is loaded too heavily in a dynamic posture, the polyurethane tread may crack. This can be mitigated past replacing the tire material with material amend suited for this awarding. Another pick is to distribute the weight differently past increasing the width of the bike or by expanding the bore of the wheel.
However, the benefits of urethane wheels far outweigh the urethane bicycle's drawbacks.
GET YOUR COMPANY LISTED BELOW
Leading Manufacturers and Suppliers
Conclusion
Urethane wheels are made of molded urethane. They come from polyurethane molding which is the process of placing a urethane polymer arrangement into a mold and allowing it to cure in social club to fabricate or manufacture plastic items. Polyurethane'southward infrequent processability makes information technology a particularly effective material in the manufacture of wheels. Polyurethane molding tin readily attain tight tolerances and complex shapes, which include urethane wheels.
Types of urethane wheels include crowned, drive, engraved, compliant, and desk. All benefits of metal, plastic, and prophylactic wheels are found in urethane wheels. They are more than affordable, more flexible, have amend noise reduction, are more resilient, and are more than impact resistant, abrasion, and corrosion than metal. In terms of low temperatures, impact, cold flow, chafe, and radiation resistance, urethane outperforms plastic. They tin can too reduce noise, are more resilient, accept superior rubberband retention, and are less expensive than plastic. All the same like any other material they take their disadvantages every bit discussed to a higher place.
Go YOUR COMPANY LISTED BELOW
Leading Manufacturers and Suppliers
Source: https://www.iqsdirectory.com/articles/polyurethane-molding/urethane-wheels.html
Posted by: connollyliffold.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Material Makes A Urethane Wheel Not Squeak For Camera Dolly"
Post a Comment